A control room is the nerve center of any organization, where various operations and...
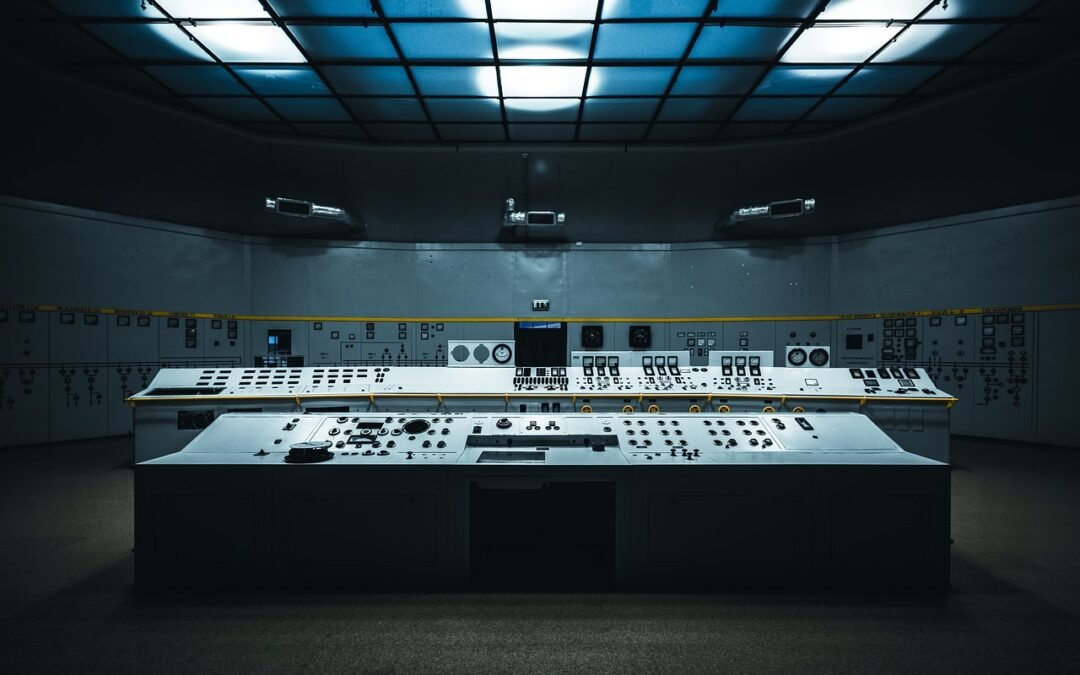


A control room is the nerve center of any organization, where various operations and...

The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding its reach, connecting everything from everyday...
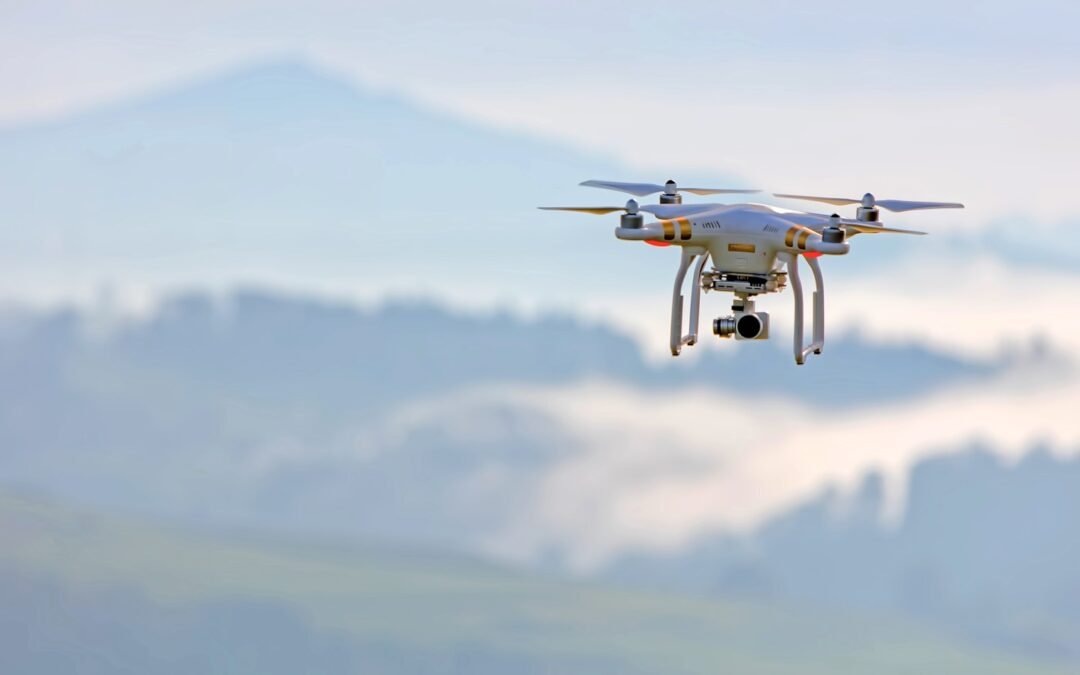

Industrial drones, also known as Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), are rapidly transforming various sectors....

In today's data-driven world, information is king. But the sheer volume of data collected...

The Internet of Things, commonly abbreviated as IoT, is a revolutionary technology that is...
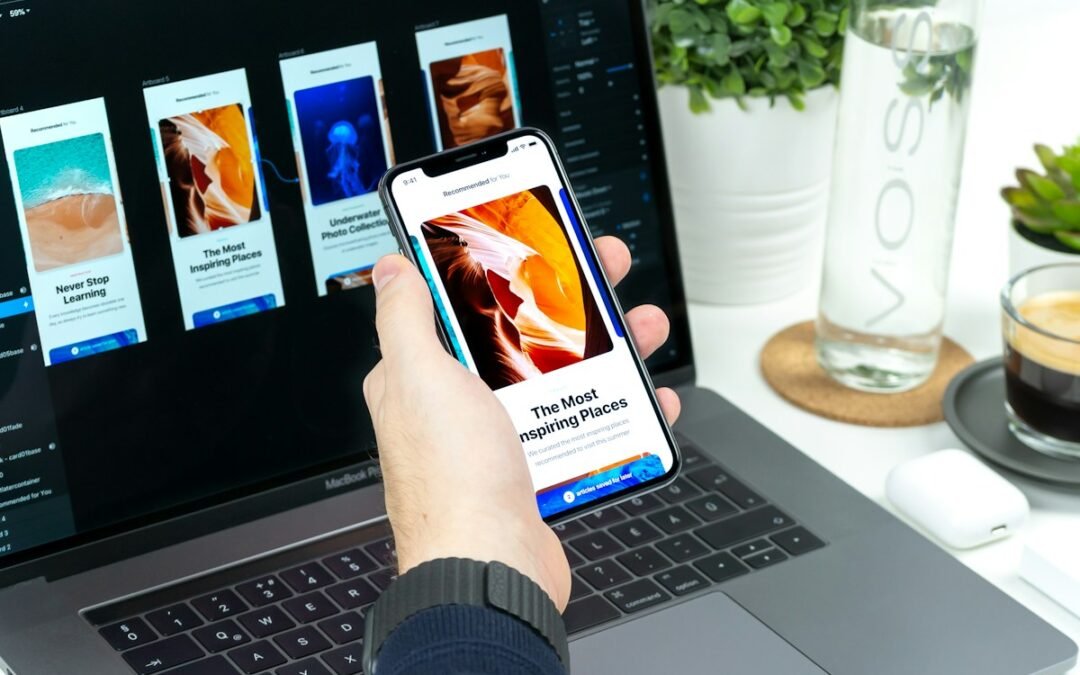
In today's digital landscape, attention spans are shorter than ever, and competition is fierce....

Embedded systems are the hidden heroes of our modern world, silently powering everything from...

Gone are the days of clunky security systems with a single blinking red light....
Revolutionize Your Smart Home with Voice-Controlled Virtual Assistants Smart home systems offer unparalleled convenience,...

Transform Your Home with Smart IoT Devices Imagine a home that anticipates your needs....