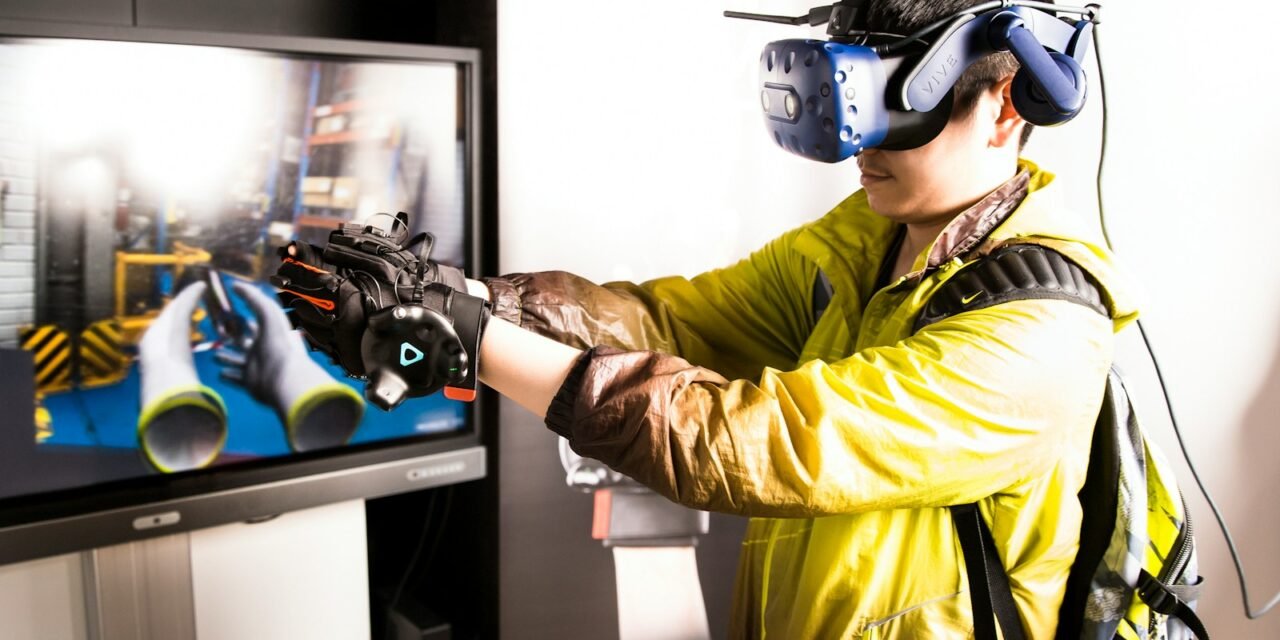
Have you ever wished you could reach into your virtual reality game and grab a sword, or feel the texture of a fabric you’re browsing online? This is where haptic technology comes in. By creating a sense of touch through vibrations, forces, and motions, haptics bridges the gap between the digital and physical worlds.

Imagine a world where you can not only see and hear virtual objects but also feel their weight, texture, and movement. This is the promise of haptic technology, which has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with machines and digital environments.
How Does It Work?
Haptic devices use a variety of methods to create tactile sensations. Here are some common approaches:
- Vibrations: This is the simplest and most common form of haptic feedback. Tiny motors in the device spin rapidly, creating a buzzing or vibrating sensation. Your smartphone’s notification alert is a basic example of this.
- Friction and Motion: Some devices use motors or gears to create pushing or pulling forces on the user’s hand. This can simulate the feeling of weight, resistance, or texture. Imagine feeling the bumpy terrain of a virtual road while racing in a VR game.
- Shape-Shifting Surfaces: These advanced interfaces use special materials that can change their shape or texture. This allows for a more nuanced and realistic touch experience, like feeling the grooves on a virtual joystick or the smooth surface of a digital button.
Where is Haptic Technology Used Today?
Haptic technology is already being used in a variety of applications, including:
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR experiences can be significantly more immersive when you can feel objects in the virtual world. Imagine feeling the recoil of a virtual gun or the resistance of climbing a virtual wall.
- Gaming Controllers: Haptic feedback in game controllers adds a layer of realism to the gaming experience. You might feel the vibration of a car engine or the jolt of getting tackled in a football game.
- Medical Training Simulators: Haptic technology allows surgeons to practice procedures on realistic virtual models, allowing them to feel the resistance of tissue or the weight of surgical instruments.
- Consumer Electronics: Even some smartphones incorporate haptic feedback for a more responsive user experience. You might feel a confirmation click when pressing a virtual button.
The Future of Haptic Technology
Haptic technology is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to become even more sophisticated and widespread in the future. Here are some exciting possibilities:
- More Realistic VR and AR Experiences: As haptic technology advances, VR and augmented reality (AR) experiences will become even more immersive and indistinguishable from the real world.
- Enhanced Product Design and Shopping: Imagine being able to virtually “feel” the texture of a piece of clothing online before you buy it. Haptics could revolutionize online shopping and product design.
- New Interfaces for Communication and Control: Haptic technology could lead to the development of entirely new ways to interact with computers and devices, creating a more intuitive and natural user experience.
As haptic technology continues to develop, the possibilities are endless. The future holds a world where touch plays a much larger role in our interactions with the digital realm, blurring the lines between the physical and virtual worlds.